The Suriname toad, scientifically known as Pipa Pipa, is a fascinating amphibian species native to the diverse landscapes of South America. This article highlights the complexities of its ecology, unique physical characteristics, feeding behavior, reproductive strategies, and challenges faced in the wild. From its special adaptation to an aquatic lifestyle to its role in cultural imagery, Pipa pipa stands out as a remarkable species in the realm of amphibians.
Ecology and Distribution:
Pipa’s preferred habitat includes slow-flowing water courses, backwaters, ponds, and ponds in the Amazon rainforest. Specially adapted for an aquatic lifestyle, this toad is virtually helpless on land. The species exhibits a wide distribution, reaching regions of Brazil and Ecuador, emphasizing its adaptability to diverse environments within South America.
Pipa pipa’s Physical Characteristics:
One of the most distinctive features of the Pipa pipa is its unusually slender and almost completely flattened body. With a broad, flat, triangular head, the toad’s appearance resembles a dull brown leaf, providing effective camouflage in its aquatic habitats. The feet, joined by star-like appendages on the front toes, further highlight its specialization for life in water. The absence of a tongue distinguishes Pipa pipa from many other frog species.
Mating and Reproduction:
Pipa’s mating season is in the fall and winter. Unlike other frogs that attract mates with croaks, male Surinamese toads produce a loud clicking sound by snapping their hyoid bone. The mating ritual involves the male grasping the female’s front legs in amplexus, causing the female’s cloaca and skin to swell.
During amplexus, a woman’s waist gradually swells. The male and female cloacae approach each other, and the eggs are transferred anteriorly to the swollen dorsal epidermis of the female. These eggs, about 6.5 mm in diameter, burrow into the skin and develop into tadpoles inside a pocket on the female’s back. Remarkably, tadpoles do not emerge as tadpoles but remain in their chambers until they reach the tadpole stage.
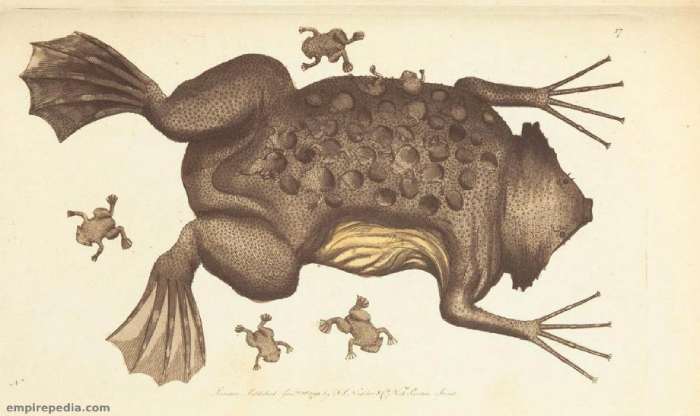
After 12 to 20 weeks, the young toads hatch as small toads, which look similar to their parents. The mother slowly sheds the thin layer of skin used for birth, and the cycle begins anew. This unique reproductive strategy sets Pipa pipa apart from many other amphibians.
Feeding Behavior:
Pipa pipa uses a specific inertial suction feeding mechanism. In water, it captures prey by entraining large volumes of water and restricting the escape of the fish with its fingers. The species uses bilateral suction, which begins by compressing its hyoid and retracting its clavicle.
The buccopharyngeal cavity connecting the mouth and throat is highly expandable, allowing the frog to enlarge it rapidly. The expansion creates negative pressure, which results in suction that draws in the water containing the prey. The prey is effectively inserted into the widened buccopharyngeal cavity, where it remains for some time before emerging through the partially open mouth.
The front hands play an important role in feeding the prey into the mouth. The forelimbs are extended and pulled toward the mouth during prey capture, held in a forward-leaning position prior to capture. This sophisticated feeding behavior demonstrates Pipa Pipa’s adaptation and efficiency as an ambush predator.
Physical Adaptations:
The Suriname toad exhibits several physiological adaptations that contribute to its unique lifestyle. The skull is hyperossified, and both the cranial and postcranial bones are highly modified compared to other anurans. While the eyes are relatively small, the species compensates with a lateral line system and neuromast organs, which help locate prey and detect predators.
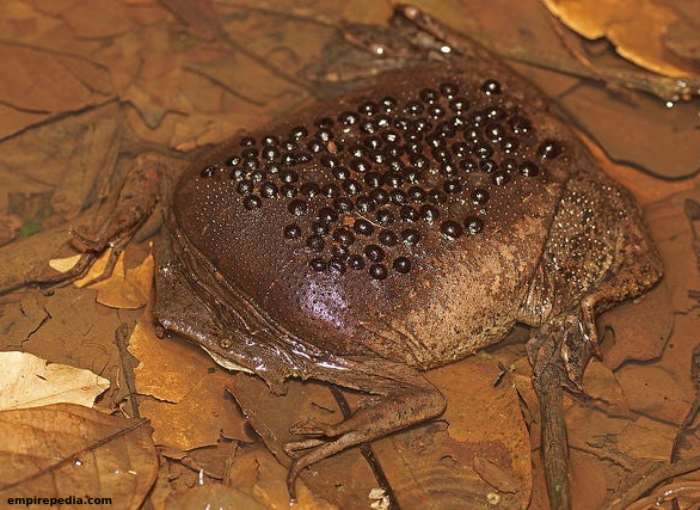

In particular, Pipa pipa lacks dermal antimicrobial peptides, potentially making it more susceptible to diseases such as chytridiomycosis and Ranavirus. Understanding these adaptations provides insight into the toad’s ecological niche and the challenges it faces in the wild.
Conservation Challenges:
Despite being classified as Least Concern by the IUCN, Pipa pipa faces threats from habitat loss and fragmentation due to agricultural expansion. Deforestation and human encroachment on the Amazon rainforest have pushed the species into regions where it is not normally encountered, emphasizing the importance of protecting its natural habitats.
Captivity and Care:
In captivity, Pipa pipa exhibits a preference for plants and rocks to hide in the aquarium. Low light conditions are necessary, and frequent water changes are necessary due to the toad’s high ammonia excretion. Challenges in captivity emphasize the need for careful consideration and understanding of species’ unique needs.
Cultural Significance:
The Suriname toad has found its place in cultural contexts, with the poet Samuel Taylor Coleridge making a sensational comparison between the multitasking nature of the toad and the hustle and bustle of ideas. Additionally, Pipa pipa is commonly cited as the trigger for trypophobia, adding a layer of intrigue to its perception in popular culture.
Conclusion:
Pipa pipa, the Surinamese toad, invites us into a world of remarkable adaptations, fascinating behaviors, and conservation challenges. As we peel back the layers of its ecology, reproduction, and feeding mechanisms, it becomes clear that this aquatic amphibian is not just a species but a testament to the miracles of evolution. Understanding and appreciating the complexities of Pipa pipa’s existence contributes to the broader tapestry of biodiversity and the need for conservation efforts to maintain its unique place in South American ecosystems.
Also, read Cuttlefish Bone: A Complete Guide To Its Fascinating History










1 comment