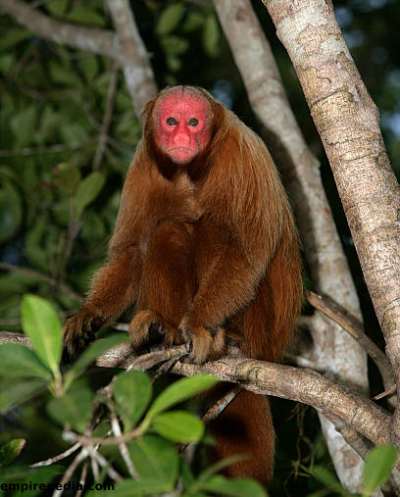
Nestled within the complex tapestry of the Amazon rainforest, the Bald uakari (Cacajao calvus) stands out as a remarkable primate, to researchers and nature enthusiasts alike. With its distinctive reddish face, bald head, and unique behavior, the Bald uakari is an iconic species of the western Amazon, living primarily in the várzea forests of Brazil and Peru. This article embarks on a journey to explore the fascinating aspects of the Bald uakari, from its physical characteristics to its important role in the ecosystem and the challenges it faces for conservation.
Taxonomy and Distribution:
Scientific Classification:
The Bald uakari belongs to the New World monkey family and is classified under the genus Cacajao. Its taxonomic lineage places it among the fascinating diversity of primate species found in the Amazon rainforest.
Geographical Range:
This species thrives in the labyrinth of the western Amazon, especially in the varzea forests near water. The bald eagle’s unique adaptations make it well-suited for life in this complex ecosystem.
Morphology and Behavior of Bald uakari:

Physical Characteristics:
Characterized by a distinctive set of features, the Bald uakari sports a short tail, a bald head, and an eye-catching crimson face. A white to red mottled coat adds to its allure. The short tail, about half the length of its body and head combined, indicates its adaptation to an aquatic lifestyle.
Patterns of Behavior:
The Bald uakari’s aquatic lifestyle is critical to its survival, especially during the rainy season when forests are flooded. In response to territorial challenges, these primates make distinctive vocalizations, tail wagging, and hair standing. Their social structure includes multi-male/multi-female groups, with females exhibiting philopatry.
Feeding Habits:
A study of the Bald uakari’s diet showed a preference for seeds (67%), fruits (18%), flowers (6%), animal prey (5%), and buds. Its powerful lower jaw, forming a pseudo-tooth comb, allows it to access hard-to-reach nuts and raw fruits. This adaptation distinguishes it from other primates and reflects its ecological niche.
Reproduction and Lifespan:
Breeding season:
Bald eagles engage in reproductive activity between October and May. The gestation period lasts about six months, which contributes to the complex dynamics of their life cycle.
Lifetime:
With a lifespan of around 30 years, the Bald uakari has remarkable longevity. Both sexes have sternal glands, which are likely involved in olfactory communication, especially during mating.
Conservation Status and Threats:

Changes in protection status:
Over the years, the Bald uakari’s conservation status has fluctuated, threatening to become vulnerable due to close migration. Despite this change, population numbers continue to decline, with a 30 percent decline over the past 30 years.
Threats to survival:
The Bald uakari faces significant threats from habitat loss and hunting. Logging activities affect forest canopies which are important for their aquatic lifestyle. Hunting by humans, especially by canoes, is a serious threat to their populations, threatening their existence.
Conservation Efforts:
Historic Preservation Measures:
Efforts such as the Brazilian Rainforest Conservation Pilot Program were initiated by the World Bank in 1999, with the goal of providing substantial funding for Amazon conservation programs. However, the effectiveness of these initial initiatives remains a subject of evaluation.
Current Conservation Programs:
Organizations such as the Wildlife Conservation Society and Brazil’s National Environmental Agency (IBAMA) are active in contemporary conservation programs. The Amazon-Andes Conservation Program, established in 2003, strives to protect key landscapes in the Amazon, which covers about three percent of the Amazon Basin.
Future Prospects and Challenges:
Ongoing Research:

Current research efforts aim to deepen our understanding of the bald eagle and its ecosystem. Ongoing studies provide valuable insight into their behavior, reproductive biology, and ecological interactions.
Challenges Ahead:
Although progress has been made in conservation, challenges remain. Deforestation, illegal logging, and human encroachment continue to pose threats. The delicate balance between conservation and human development in the Amazon remains a complex challenge.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Bald uakari emerges as a charismatic species that embodies the richness of the Amazon rainforest. Its distinctive features, combined with its important ecological role, highlight the importance of concerted conservation efforts. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of this red-faced wonder, our responsibility to protect its habitat becomes increasingly important, ensuring that the Bald uakari remains an enduring symbol of biodiversity. is what surrounds the heart of the Amazon.
Also, read Ecology, Behavior, and Conservation of the Suriname Toad